Klippel-Feil syndrome
What is a Klippel-Feil syndrome? It is a musculoskeletal defect characterized by union of two vertebrae in the neck. KFS is a congenital and genetic in nature, which means that the patient has it at birth. Klippel-Feil syndrome is a disease itself, but it can also be associated with other conditions such as hemifacial microsomia and Wildervanck syndrome. (1, 2, and 3)
picture 1: An adult with a KFS.
image source: globalgenes.org
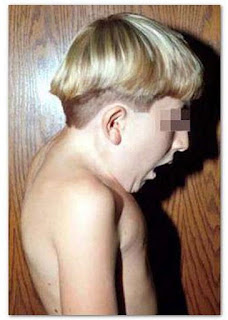
Picture 2: A pediatric patient suffering from KFS.
image source: wikimedia.org
Klippel-Feil syndrome classifications
Picture 3: An infant born with KFS.
image source: jcnonweb.com
- Type I - There is an extreme fusion of the cervical spine.
- Type II - One or two cervical vertebrae are fused.
- Type III - Either type I or II Klippel-Feil syndrome along with problems in the lumbar and thoracic spine. (3,4)
Klippel-Feil syndrome symptoms
picture 4: A patient demonstrating the cardinal symptoms od KFS.
image source: ars.els-cdn.com
picture 5: A curvature of the spine is one of the cardinal signs of KFS.
image source: upload.orthobullets.com
picture 6: An infant with a severe case of KFS.
image source: syndromespedia.com
The three most common signs and symptoms of Klippel syndrome are a short neck, low posterior hairline, and limited range of motion of the neck. These are called the Klippel-Feil syndrome triad. Other symptoms to watch out for include:
- fusion of at least two spinal bones in the neck
- crooked/twisted neck
- congenital scoliosis (deviation of the spine)
- respiratory-related issues
- neurological problems (4)
- spina bifida (insufficient closing in utero of the neural tube)
- hearing difficulties
- cleft palate (4)
- syndactyly (webbed fingers)
What causes Klippel-Feil syndrome?
Up to this time, it is still unclear as to what really is the exact cause of Klippel syndrome. Medical experts believed that it has something to do with the mutations of GDF6 and GDF3 genes.How to diagnose Klippel-Feil syndrome?
The patient's past medical and surgical history will be thoroughly investigated. An in-depth physical exam is performed by the examining physician. To confirm the diagnosis of Klippel-Feil syndrome numerous tests and procedures are performed. They are the following:- X-ray of the neck, spine, and scapula
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- CT scan (Computed Tomography)
- Genetic Testing (5)
- EOS Imaging
- Ultrasound
- Cardiac Evaluation
- Hearing Test (5)
picture 7: A radiologic image of a patient with KFS
image source: images.radiopaedia.org
image source: images.radiopaedia.org
Klippel-Feil syndrome treatment
Unfortunately, there is no treatment yet for Klippel-Feil syndrome. Medical professionals focused on the symptomatic relief. The patient needs to be seen by a team of medical professionals such as surgeons, therapists, nurse, and psychologist. The immediate family members should also be actively involved in the patient's care. (5, 6)
picture 8: A supportive care in a patient with KFS
image source: media-cdn.timesfreepress.com
image source: media-cdn.timesfreepress.com
picture 9: A young patient with KFS.
image source: straightfromthedoc.com
image source: straightfromthedoc.com
Klippel-Feil syndrome life expectancy
A patient with a Klippel-Feil syndrome has a normal life expectancy. Although the integrity of life may be affected, especially if the symptoms and complications are not dealt with right away. (6, 7)
Klippel syndrome complications
The complications are mainly neurologic in nature. Hence, the patient should be closely monitored and is strongly advised to avoid activities that could further cause injury or trauma to the cervical vertebrae. (6, 7)
picture 10: A patient with KFS with hearing difficulties.
image source: adc.bmj.com
image source: adc.bmj.com
Klippel Feil Syndrome prognosis
The prognosis of people with Klippel Feil syndrome primarily depends on the severity of the patient's condition. People with mild Klippel Feil syndrome can lead a normal life. However, those with severe complications need a routine check-up. Overall, the prognosis is good for as long as the complications are managed properly. (8, 9, and 10)
References
- https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/klippel-feil-syndrome
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1264848-overview
- https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/klippel-feil-syndrome
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Klippel%E2%80%93Feil_syndrome
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/klippel-feil-syndrome-3
- https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/klippel-feil-syndrome/
- https://www.orthobullets.com/spine/2051/klippel-feil-syndrome
- http://www.chop.edu/conditions-diseases/klippel-feil-syndrome
- https://www.physio-pedia.com/Klippel-Feil_syndrome
- https://www.webmd.com/children/klippel-feil-syndrome